The ideal argon pressure for MIG welding typically ranges between 15 to 25 cubic feet per hour (cfh). Maintaining proper argon gas flow is crucial for weld quality.
Argon gas plays an essential role in MIG welding, providing the inert atmosphere necessary to protect the weld pool from contaminants. As an industry standard, welders rely on a precise argon flow rate to ensure consistent, high-quality welds. Adjusting the pressure according to the specific welding situation, such as the type of metal or thickness, can also affect the outcome.
By keeping within the recommended range, welders can avoid common issues like porosity or excessive spatter. Understanding and measuring the correct argon pressure is a fundamental skill for professional welders striving for optimal welding performance and integrity.
Role Of Argon Gas
Think of argon gas as a protective shield for metals during MIG welding. This invisible defender plays a crucial role. Let’s explore how argon guards and perfects the welding process.
Argon gas acts like a strong wall around the welding spot. It keeps the area safe from harmful air and gases. Imagine a bubble protecting the hot, molten metal as it fuses together.
- Stabilizes the arc: Argon makes the electric arc smooth and steady.
- Controls the weld pool: The gas helps shape the molten metal neatly.
- Avoids spatter: Less spatter means a cleaner weld and less cleanup.
Argon prevents rust before it can start. When metal heats up, it loves to react with oxygen. Argon stops this from happening.
| Action | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Pushes oxygen away | Keeps the weld area clean from rust. |
| Creates an inert atmosphere | Metal stays strong and pure. |
Welds stay shiny and free from crusty, weak spots. The result is a strong bond that lasts.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Factors Affecting Argon Pressure
When diving into the world of MIG welding, understanding the role of argon gas pressure is crucial. The right pressure ensures optimal gas coverage, which shields the weld from contaminants. Several key factors influence the argon pressure you need. Let’s explore some of these factors that are essential for achieving the perfect weld.
Material Thickness
The thickness of the material you’re welding has a direct impact on argon pressure. Thicker materials require more argon to protect the larger molten pool.
Thin materials: Lower pressure to prevent burn-through.
Thick materials: Higher pressure to ensure adequate coverage.
Welding Position
Your welding position plays a role in how gravity affects the gas coverage.
- Flat: Standard pressure settings work well.
- Vertical or overhead: Adjust pressure to combat gravity.
Welding Wire Diameter
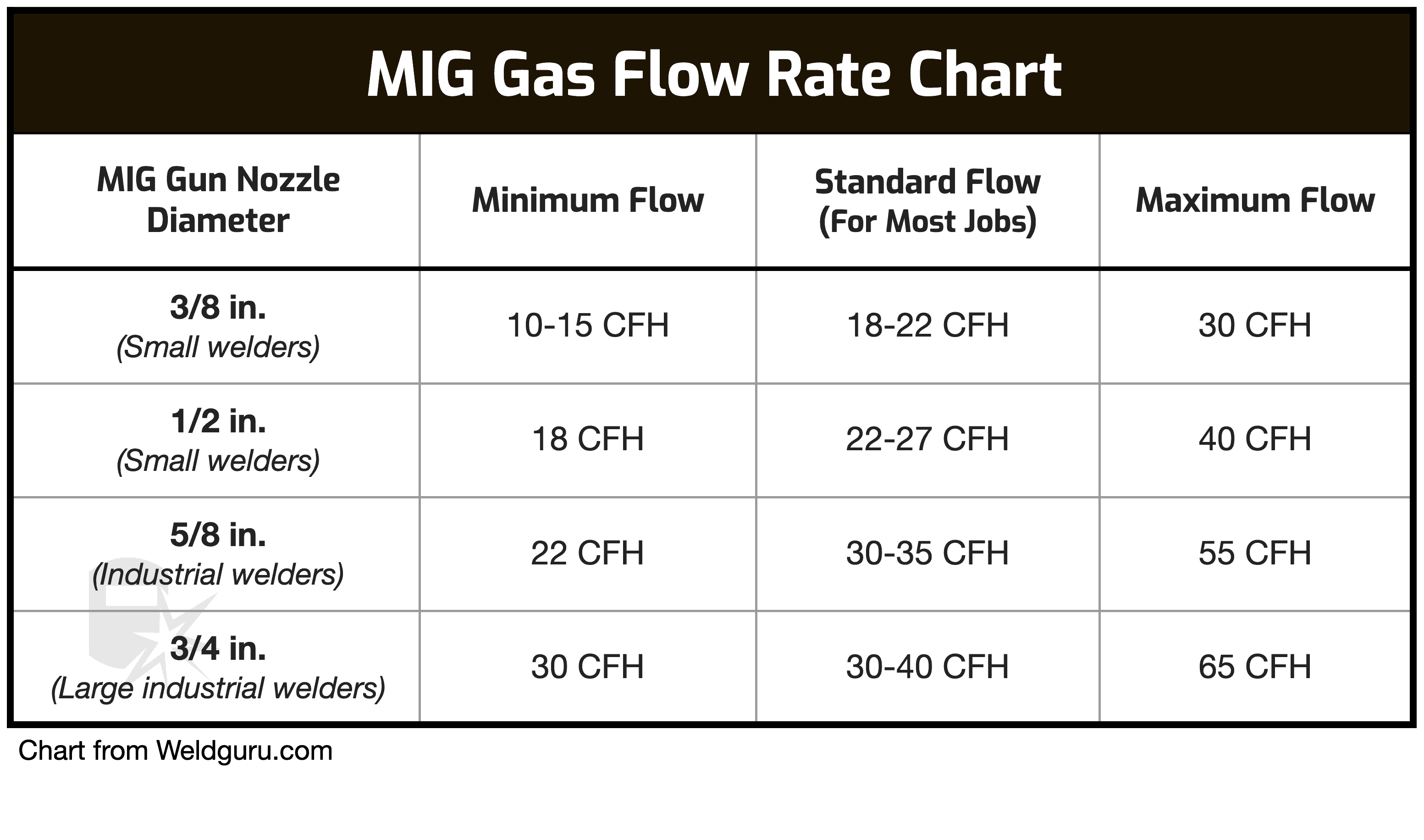
The wire’s diameter determines the argon flow rate—finer wires need less argon.
| Wire Diameter | Argon Pressure (CFH) |
|---|---|
| 0.023 inches | 20-25 |
| 0.030 inches | 25-30 |
| 0.035 inches | 30-35 |
| 0.045 inches | 35-40 |
Optimizing Argon Pressure
Mastering the art of argon pressure is crucial for superior MIG welding results. Argon acts as a shield gas, protecting the weld area from atmospheric gases that could corrupt the weld. Discovering the optimal argon flow rate lays the foundation for a flawless, spatter-free weld.
Choosing The Right Flow Rate
Selecting the perfect flow rate ensures a consistent weld. Too much argon wastes gas and money. Too little exposes the weld to contamination. Aim for a flow generally between 15 to 25 cubic feet per hour (CFH). The specific project dictates the exact rate.
- Thin materials – Lean toward the lower end of the scale.
- Thicker sections – Require more gas for proper coverage.
Adjusting For Different Welding Conditions
Varying welding scenarios demand distinct argon flow adjustments:
| Condition | Flow Adjustment |
|---|---|
| Wind or Drafts | Increase flow slightly to counteract dispersal. |
| Tight Spaces | Decrease flow to prevent gas buildup and turbulence. |
| Welding Position | Vertical or overhead welding may need more flow. |
Regular monitoring and adjustment ensure consistent high-quality welds under various conditions.
Credit: weldguru.com

Credit: www.westermans.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Argon Pressure For Mig Welding
What Pressure Should The Gas Be On A Mig Welder?
The ideal gas pressure for a MIG welder typically ranges between 15 and 25 cubic feet per hour (CFH). Adjust based on material thickness and type.
What Should Gas Flow Be For Mig Welding?
The recommended gas flow rate for MIG welding typically ranges between 20-25 cubic feet per hour (CFH). Adjust this flow to suit the specific welding environment and application.
How Much Argon Should I Use When Mig Welding?
For MIG welding, typically use 20-25 cubic feet per hour of argon for optimal results. Adjust based on material thickness and weld quality.
What Is The Recommended Regulator Line Pressure Psi For Mig Welding?
The recommended regulator line pressure for MIG welding typically ranges from 20 to 30 psi. Always consult your welder’s manual for specific recommendations.
Conclusion
Understanding the right argon pressure for MIG welding is vital for optimal results. Mastering this ensures stronger welds and a flawless finish. Remember, precision is key. Before your next welding project, double-check your gas flow rates. Embrace the skill, and weld with confidence!
