To increase the duty cycle of a welder, enhance its cooling mechanisms and lower the ambient temperature. Avoid exceeding the machine’s recommended settings for current and duration.
Exploring ways to boost the duty cycle of a welding machine is crucial for efficiently handling larger, more demanding projects. A higher duty cycle means the welder can operate longer without overheating, making it a desirable feature for professionals and hobbyists alike.
Upgrading the cooling system plays a significant role, as it allows the device to dissipate heat more effectively. This can include improving the fan quality or adding supplementary cooling equipment. Lowering the working environment temperature will also contribute to cooler operating conditions. Maintaining the welder within its optimal performance range will ensure longevity and consistent output. It’s vital that users adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevent any damage to the components or compromising safety standards. Bridging practical enhancements with operational best practices translates into a stable increase in a welder’s duty cycle.
Credit: www.forconstructionpros.com
Benefits Of Increasing Duty Cycle
The duty cycle of a welder is crucial for its performance. When the duty cycle increases, a welder can operate longer at a given amperage without overheating. This brings several benefits, such as reducing downtime and improving productivity.
Reduced Downtime
Less time waiting, more time welding. By increasing a welder’s duty cycle, the need for cooling periods diminishes. This means that a welder can be used more extensively during any given work period. As a result, there are fewer interruptions, leading to the completion of tasks without needless pauses.
Improved Productivity
The length of uninterrupted welding stretches with a higher duty cycle. Projects advance faster. This efficiency leads to more completed welds in a day. Workers achieve targets quicker, which can also lead to cost savings in labor. More welding, better results, and satisfied clients make for good business.
| Aspect | With Standard Duty Cycle | With Increased Duty Cycle |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Time | Limited | Extended |
| Cool Down Time | Required More Often | Required Less Often |
| Project Completion | Slower | Quicker |
- Continuous welding without frequent stops
- Increased operational efficiency during work hours
- Faster project turnover, leading to more business
Factors Affecting Duty Cycle
Understanding the Factors Affecting Duty Cycle is key to increasing the efficiency of a welder. The duty cycle represents the amount of time a welder can operate safely before needing to cool down. Here, we delve into pivotal components such as Heat Dissipation and Power Supply, and how each influences the welder’s operational capacity.
Heat Dissipation
Better heat dissipation means a higher duty cycle. Several factors contribute to effective cooling:
- Cooling Systems: Utilize fans or liquid coolants for efficient heat removal.
- Welder Design: Designs with larger surface areas release heat quicker.
- Ambient Temperature: Cooler environments aid in reducing welder heat.
Implementing enhanced cooling mechanisms directly impacts the welder’s ability to maintain performance over longer periods.
Power Supply
The power source used is fundamental in determining the duty cycle. Keep an eye on these aspects:
| Voltage Stability | Amperage Output |
|---|---|
| Consistent voltage ensures stable performance. | Higher amperage units may have improved duty cycles. |
Select a power supply that complements the welder’s specifications to maximize the duty cycle.
Methods To Increase Duty Cycle
Duty cycle measures how long a welder can run within a certain period. Increasing this helps you weld for more time without your machine overheating. Let’s dive into methods to boost your welder’s duty cycle.
Enhancing Cooling Systems
Keeping your welder cool is key to a higher duty cycle. More efficient cooling means longer welding times. Here are the steps to upgrade your cooler:
- Install a fan – boosts air circulation around the welder.
- Use a larger radiator – dissipates heat faster.
- Upgrade your coolant – better quality for lower temperatures.
Optimizing Power Settings
Adjusting the power output is another way to increase duty cycle. These tips ensure you use power effectively:
- Use lower amperage for thinner materials.
- Ensure your power supply matches the welder’s optimum ratings.
- Adjust the settings according to your welding technique.
Common Challenges & Risks
Common Challenges & Risks with enhancing a welder’s duty cycle often revolve around overheating and safety. As we push our welders to do more, we must also consider how to protect them and the operators from potential harm. This includes managing the heat generated and adhering to rigorous safety protocols.
Overheating
Overheating is a top challenge when trying to increase a welder’s duty cycle. Welders generate immense heat, and pushing them beyond their limits can lead to several issues. A hot welder can malfunction or suffer long-term damage. Recognizing this, consider the following points:
- Adequate Cooling: Ensure the machine has proper cooling mechanisms and downtime.
- Monitor Temperature: Regularly check the temperature during extended use.
- Maintain Equipment: Keep parts clean and in good condition to improve heat dissipation.
Safety Considerations
Safety Considerations become even more crucial as you try to expand the duty cycle of your welder. Increased operation times can increase the risk of accidents. See the safety measures below:
| Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Regular Breaks | Prevent operator fatigue. |
| Protective Gear | Shield users from sparks and heat. |
| Proper Training | Ensure users know how to handle the welder safely. |
Tips For Increasing Duty Cycle
Welders need high duty cycles for tough jobs. A higher duty cycle means more welding, less waiting. Want a stronger machine? Take these steps.
Regular Maintenance
Keep your welder clean and check parts often. Dirt causes overheating. That cuts the duty cycle. Look at these points:
- Check cables for damage.
- Clean dust and dirt from vents.
- Ensure connections are tight.
- Replace worn parts, like contact tips.
Regular care makes a big difference.
Proper Welding Techniques
Good technique makes your welder last. Make these habits:
- Prep materials well. Clean metals weld better.
- Use the right settings for the job.
- Weld in short bursts when needed.
- Allow cool-down time between long welds.
These tips help prevent overheating. That boosts your duty cycle.

Credit: www.wire-wizard.com
Credit: weldguru.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of How To Increase Duty Cycle Of A Welder
What Is A Good Duty Cycle For A Welder?
A good duty cycle for a welder typically ranges from 20% to 60%, depending on the welder’s power and the intended usage. High-end industrial welders may offer higher duty cycles for continuous use.
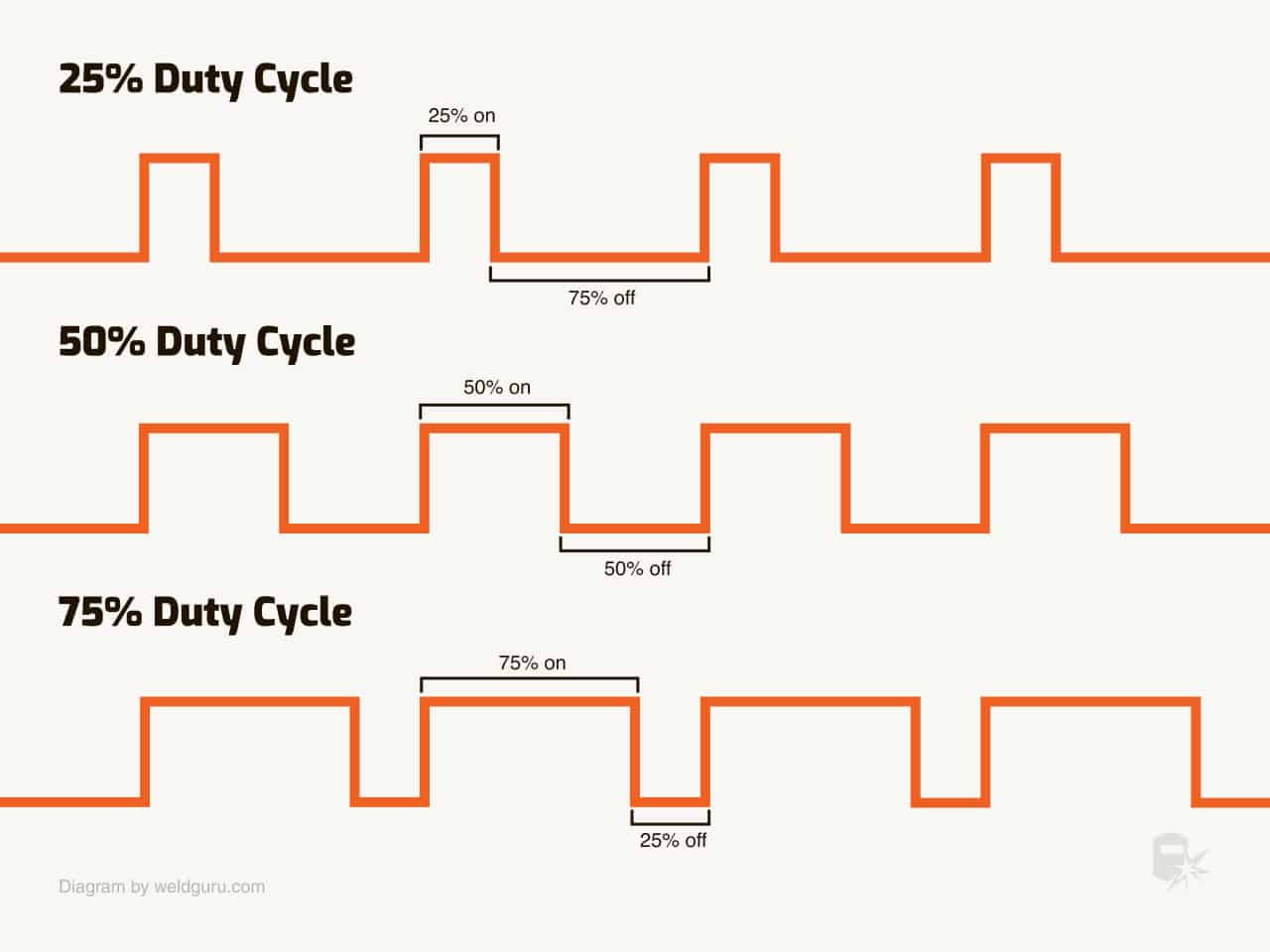
How Long Can You Weld With A 60% Duty Cycle?
With a 60% duty cycle, you can weld continuously for 6 minutes and then rest for 4 minutes to prevent overheating. This pattern maintains the welder’s efficiency and longevity.
What Does 20% Duty Cycle Mean?
A 20% duty cycle means a device operates for 20% of a given period, then rests for the remaining 80%. For instance, in a 10-minute cycle, it runs for 2 minutes and rests for 8 minutes.
What Is 80 Percent Duty Cycle Welder?
An 80 percent duty cycle welder can operate continuously for 8 minutes out of a 10-minute period before needing a cooldown to prevent overheating.
Conclusion
In essence, enhancing your welder’s duty cycle is an achievable goal. By maintaining your equipment, selecting the right welder, and following best practices, longevity in welding operations is within reach. With these strategies in hand, expect to see improved performance and productivity in all your welding projects.
Remember, regular maintenance is the key to sustained success.