Porosity in welding refers to the presence of tiny holes or voids in the weld metal. These cavities can weaken the weld and may lead to failure.
Porosity is a common flaw that occurs during the welding process when gas gets trapped in the solidifying metal. It is imperative for welders to prevent or minimize this issue to ensure the integrity and strength of the weld joint.
The causes of porosity include contamination on the material’s surface, improper welding technique, or incorrect equipment settings. Identifying and addressing these causes are essential steps in ensuring a durable and safe weld. It is critical that welders are skilled and knowledgeable about the materials and techniques they use to prevent such imperfections. Mastery of welding practices and adherence to proper guidelines can significantly reduce the chances of porosity and produce high-quality welds.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Causes Of Porosity In Welding
Understanding the Causes of Porosity in Welding is vital for professionals aiming to achieve strong and reliable welds. Porosity, akin to pockets of air trapped in the weld metal, can compromise the integrity and strength of the welded joint. These irregularities often stem from a range of factors during the welding process. Let’s examine the primary culprits behind porosity, so welders can tackle these issues head-on and improve their craftsmanship.
Moisture Contamination
- Electrode Storage: Unsealed or improperly stored electrodes absorb moisture.
- Material Surface: Damp material surfaces introduce hydrogen into the weld pool.
- Ambient Humidity: High humidity levels contribute to moisture in the welding environment.
Gas Contamination
Various gases in the workshop atmosphere, like oxygen or carbon dioxide, can infiltrate the weld area. These gases often react with the welding metal, leading to the formation of gas pockets or porosity.
| Contaminant Gas | Source |
|---|---|
| Oxygen | Surrounding air |
| Carbon Dioxide | Combustion, Respiratory processes |
Improper Shielding Gas
The role of shielding gas in the welding process is to protect the molten weld pool from the surrounding atmosphere. Insufficient or incorrect shielding gas often creates porosity. Following are key practices to prevent this issue:
- Gas Flow Rate Check: Ensure the gas flow is adequate and consistent.
- Tight Connections: Confirm all gas supply lines are secure with no leaks.
- Appropriate Gas: Use the correct type based on the welding application.
Detecting Porosity In Welds
Discovering holes in welds, known as porosity, is key for strong joints. These unwelcome air pockets can weaken your welding project. Let’s explore effective ways to spot these sneaky imperfections.
Visual Inspection
Eyes can catch many weld flaws. A shiny surface with tiny holes hints at porosity. The size, number, and distribution of these holes can tell experts about the weld’s overall health.
- Clean the weld before inspecting.
- Use good lighting to spot defects easily.
- Look for irregular shapes that don’t blend smoothly.
Non-destructive Testing
For hidden porosity, special tests are a must. These methods don’t hurt the weld and provide in-depth analysis.
| Type of Test | How it Works |
|---|---|
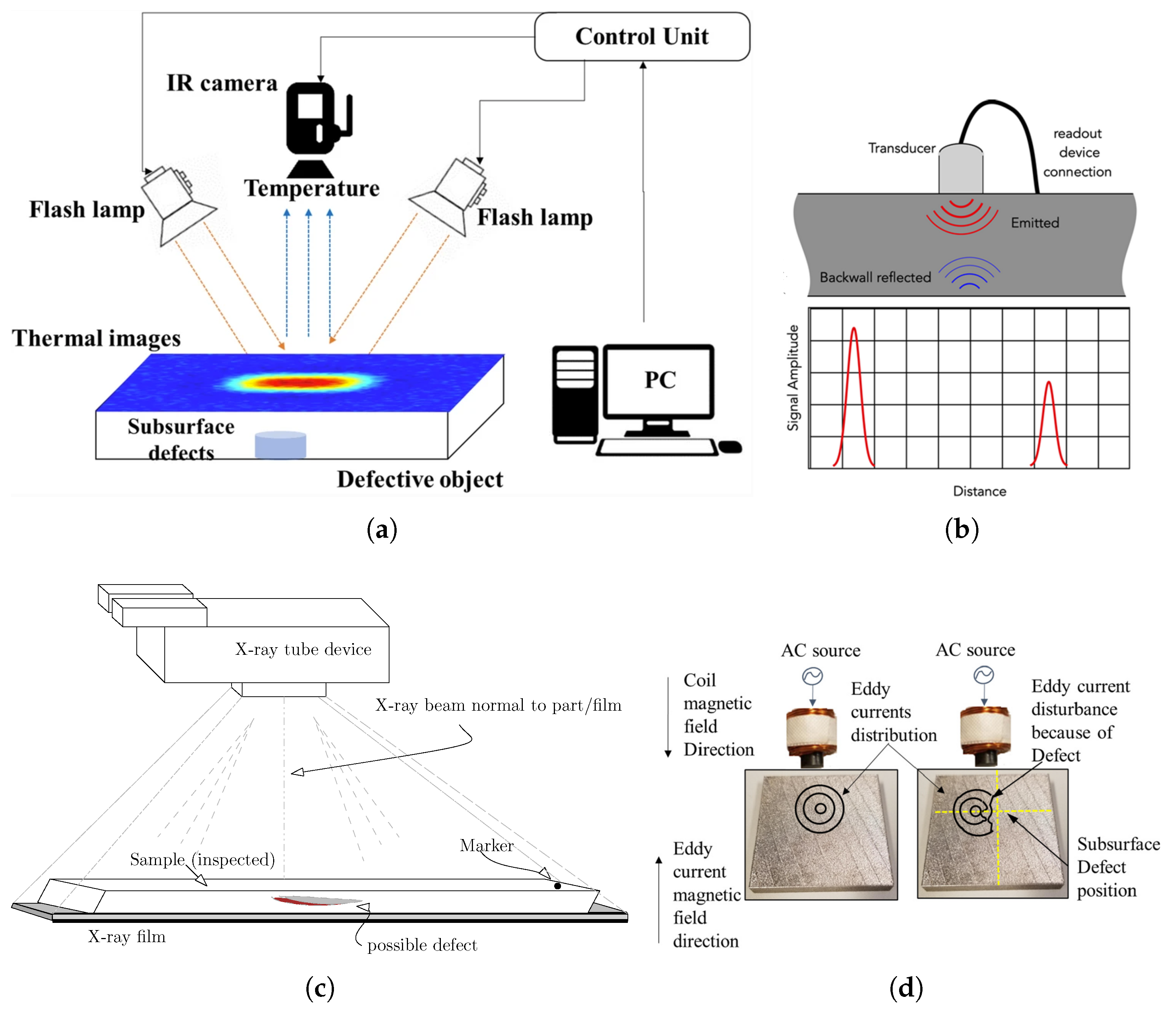
| X-ray Testing | Shows shadows where holes are. |
| Ultrasonic Testing | Uses sound waves to find gaps. |
| Liquid Penetrant Testing | Dye seeps into holes, revealing them. |
All these tests need trained operators. They help spot porosity early on. This way, welds stay safe and strong.
Preventing And Minimizing Porosity
Porosity in welding happens when gas gets trapped in weld metal. It can weaken the weld. But, you can stop it. So, your welds stay strong and good looking.
Proper Welding Technique
- Keep it steady: Move your hand slow and smooth.
- Right angles: Hold the torch just right, not too tilted.
- Perfect speed: Not too fast, not too slow, find the sweet spot.
Optimal Shielding Gas
| Gas Mix | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Argon | Clean, less spatter |
| CO2 | Deeper penetration |
Use the right gas mix. It protects the weld from air, stopping porosity.
Control Moisture Contamination
- Store rods dry: Wet rods can cause gas pockets.
- Clean metals: Get rid of any rust or oil on your metal.
- Dry before welding: Make sure your metal is dry.
Credit: www.slideshare.net

Credit: m.facebook.com
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is Porosity In Welding
What Causes Porosity In?
Porosity in materials typically originates from trapped air, gases, or contaminants during the manufacturing process. Incorrect cooling rates or material handling can also contribute to porosity.
What Is The Defect Of Porosity?
Porosity defects weaken material strength and may cause leaks in pressure-containing applications. These defects reduce durability and can compromise the structural integrity of castings or welds.
Can You Burn Porosity Out Of A Weld?
No, you cannot burn porosity out of a weld. Porosity must be prevented through proper technique or repaired by grinding out and rewelding.
Why Am I Getting Porosity With 7018?
Porosity with 7018 electrodes often results from moisture contamination, improper storage, or incorrect welding techniques. Ensure rods are dry and welding parameters are correct to prevent this issue.
Conclusion
Understanding porosity in welding is crucial for achieving structural integrity and optimum performance. Mastery over this aspect leads to durable and reliable welds. As welders confront porosity, the value of skilled technique and proper material selection becomes evident. Embrace these insights for standout welding outcomes and set the standard for excellence in your work.
