Dual Shield Welding is a process that uses a flux-cored wire and external gas shielding. It’s a subtype of FCAW (Flux-Cored Arc Welding), combining benefits of both stick welding and MIG welding.
Dual Shield Welding presents itself as a versatile and powerful method used in the industry. It achieves high deposition rates while ensuring smoother welds and greater penetration. This approach can be used on thicker metals and is particularly known for its efficiency and strength.
Dual Shield Welding works well in various positions, making it suitable for complex projects. Workers often prefer it for its adaptability in different environments, including outdoors where wind might disrupt gas shielding. It is a choice method where productivity and strong welds are essential, such as in construction and heavy equipment repair. With its combination of speed and quality, Dual Shield Welding remains a popular choice for professional welders.
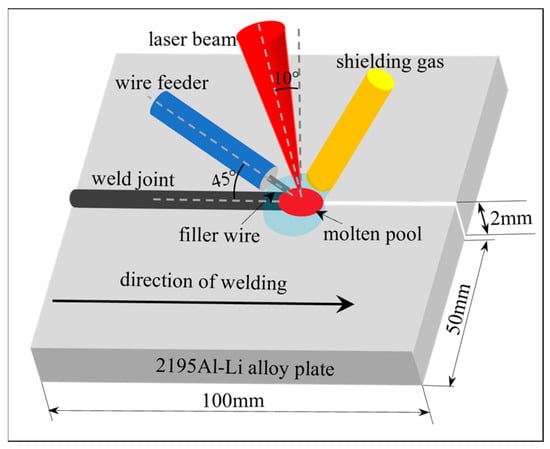
Credit: www.mdpi.com
How Dual Shield Welding Works
Understanding how dual shield welding operates is the key to harnessing its benefits.
Description Of Dual Shield Welding Process
Dual Shield Welding, also known as Flux Cored Arc Welding with an External Shielding Gas, combines two shielding methods. This process uses a flux-cored wire and an external shielding gas to protect the weld pool from contamination.
- Flux inside the wire: Produces gas and slag to shield the weld
- External gas: Adds another layer of protection
Components And Materials Used In Dual Shield Welding
| Component/Material | Function |
|---|---|
| Flux-cored wire | Carries current, forms arc, adds filler metal |
| Shielding gas | Protects weld area from air |
| Power source | Supplies electricity for welding |
| Welding gun | Controls wire feed and arc |

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Advantages Of Dual Shield Welding
Dual Shield Welding combines the benefits of MIG and flux-cored welding. It uses a continuous wire feed, a shielding gas, and flux inside the wire to protect the weld pool. This advanced welding technique offers numerous advantages discussed below.
Increased Efficiency
Dual Shield Welding ramps up productivity with its high deposition rates. It allows welders to lay more weld metal in a shorter time. This translates to faster project completion. Here’s how Dual Shield Welding streamlines operations:
- Higher deposition rates: Faster than most traditional methods.
- Less welding time: Quicker jobs, boosting overall throughput.
- Reduced cleanup: Minimal slag eases post-weld activities.
Enhanced Weld Quality
With Dual Shield Welding, expect superior welds that meet rigorous standards. This method minimizes defects that could weaken the weld. Benefits include:
| Feature | Impact on Weld Quality |
|---|---|
| Deep penetration | Creates stronger joints, especially on thick materials. |
| Smooth arc | Produces cleaner welds with a visually appealing finish. |
| Low spatter | Results in a neat final product with less post-weld grinding. |
Applications Of Dual Shield Welding
Dual Shield Welding combines flux-cored wire with an external gas shield. This technique is known for deep penetration, high deposition rates and smooth bead appearance. Here are the key applications where Dual Shield Welding shines:
Industrial Applications
Industrial Applications
Dual Shield Welding is widely used in heavy industries. Industries demand strong welds for large-scale projects, and this method delivers that. See how:
- Manufacturing Equipment: Used in making machines that build other products.
- Shipbuilding: Offers robust welds for ships that face fierce seas.
- Pipeline Construction: Pipes carry resources with no leaks due to strong welds.
Construction Applications
Construction Applications
The construction sector benefits greatly from Dual Shield Welding. Its high efficiency makes it perfect for outdoor work, even in windy conditions:
- Building Structures: Creates the steel framework for skyscrapers.
- Bridge Construction: Joins large metal sections to span vast distances.
- Infrastructure Projects: Supports the growth of urban landscapes.
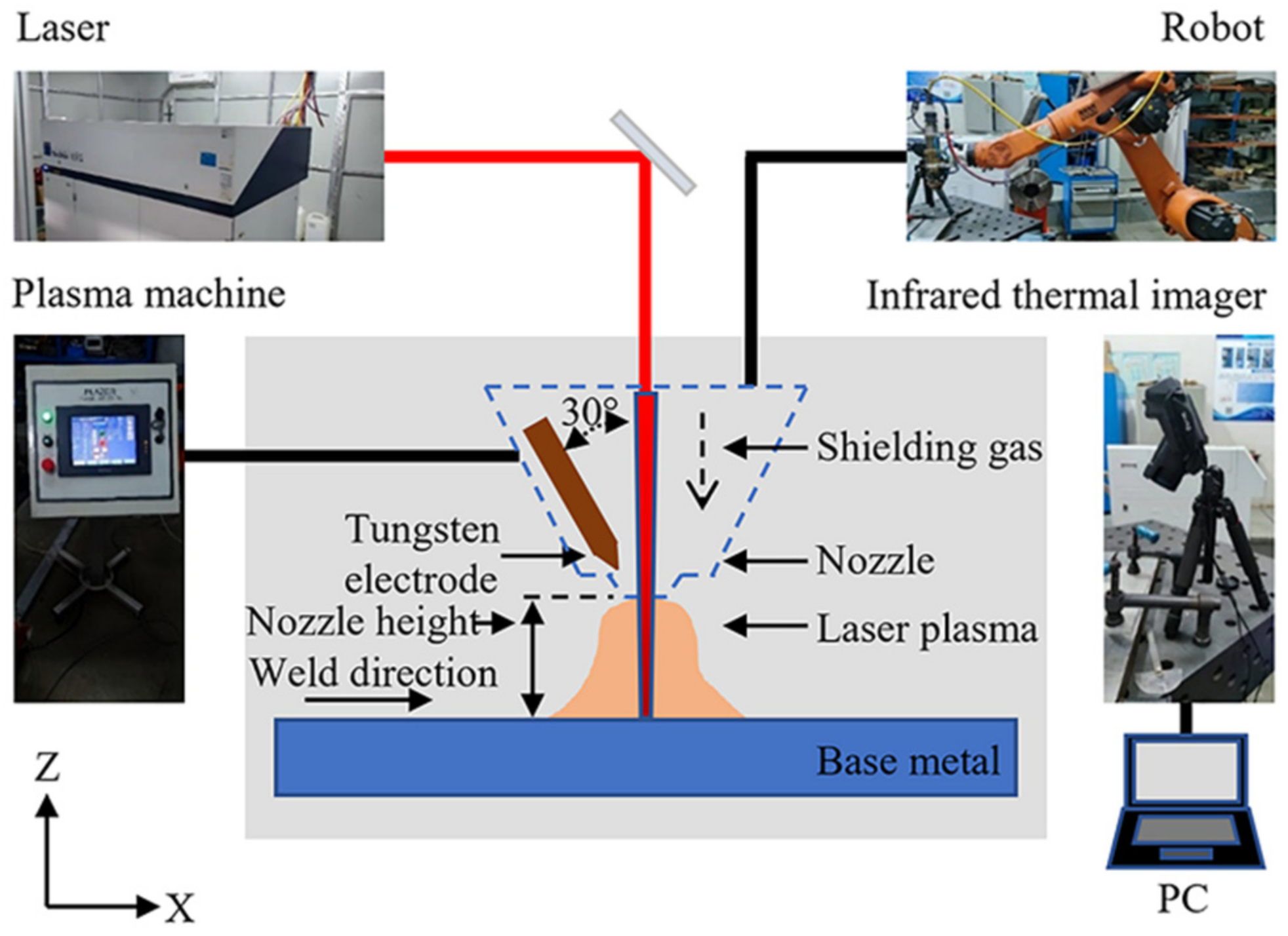
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Challenges And Best Practices
Mastering the art of Dual Shield Welding combines knowledge with skill. This process, also known as Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) with an additional shielding gas, produces strong welds quickly. Yet, it’s not without its challenges. Identifying these and adhering to best practices will ensure a successful weld. Let’s delve into the common hurdles and tips for excellence in Dual Shield Welding.
Common Challenges in Dual Shield Welding
Common Challenges In Dual Shield Welding
Understanding the obstacles can transform a good weld into a great one. Here are a few challenges welders often face:
- Equipment Set-Up: Getting the right balance of voltage, amperage, and feed speed is crucial.
- Gas Selection: Choosing the correct shielding gas composition affects weld quality.
- Welding Technique: Maintaining the proper stick-out length and travel speed is essential.
- Environmental Conditions: Wind can disrupt gas shielding, leading to defects.
Best Practices for Successful Dual Shield Welding
Best Practices For Successful Dual Shield Welding
Follow these best practices to tackle the challenges and achieve strong, clean welds every time:
- Prep Your Work Area: Ensure a wind-free environment or employ wind blocks.
- Tune Your Equipment: Calibrate the welder settings before starting your project.
- Select the Right Gas: Use a combination of CO2 and Argon for most applications.
- Weld in Suitable Positions: Adjust the weld piece to avoid welding overhead when possible.
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is Dual Shield Welding
What Wire Do You Use For Dual Shield Welding?
For dual shield welding, use a flux-cored wire specifically designed for this process, typically an E71T-1 or similar type.
Is Dual Shield A Dcep?
Yes, dual shield welding typically uses Direct Current Electrode Positive (DCEP).
What Polarity Is Dual Shield Welding?
Dual shield welding typically uses direct current electrode positive (DCEP) polarity.
What Causes Worm Holes In Dual Shield Welding?
Wormholes in dual shield welding result from trapped gas in the solidifying weld, often caused by surface contamination or thick coatings.
Conclusion
Dual shield welding stands out for its versatility, efficiency, and strong results. This method blends the benefits of both MIG and flux core welding, offering a robust solution for industrial needs. It excels in various environments, making it a favorite among professionals seeking precision and strength.
By understanding its techniques and applications, welders can harness the full potential of dual shield welding for superior craftsmanship. Embrace the power of this dynamic process to enhance your welding projects.
